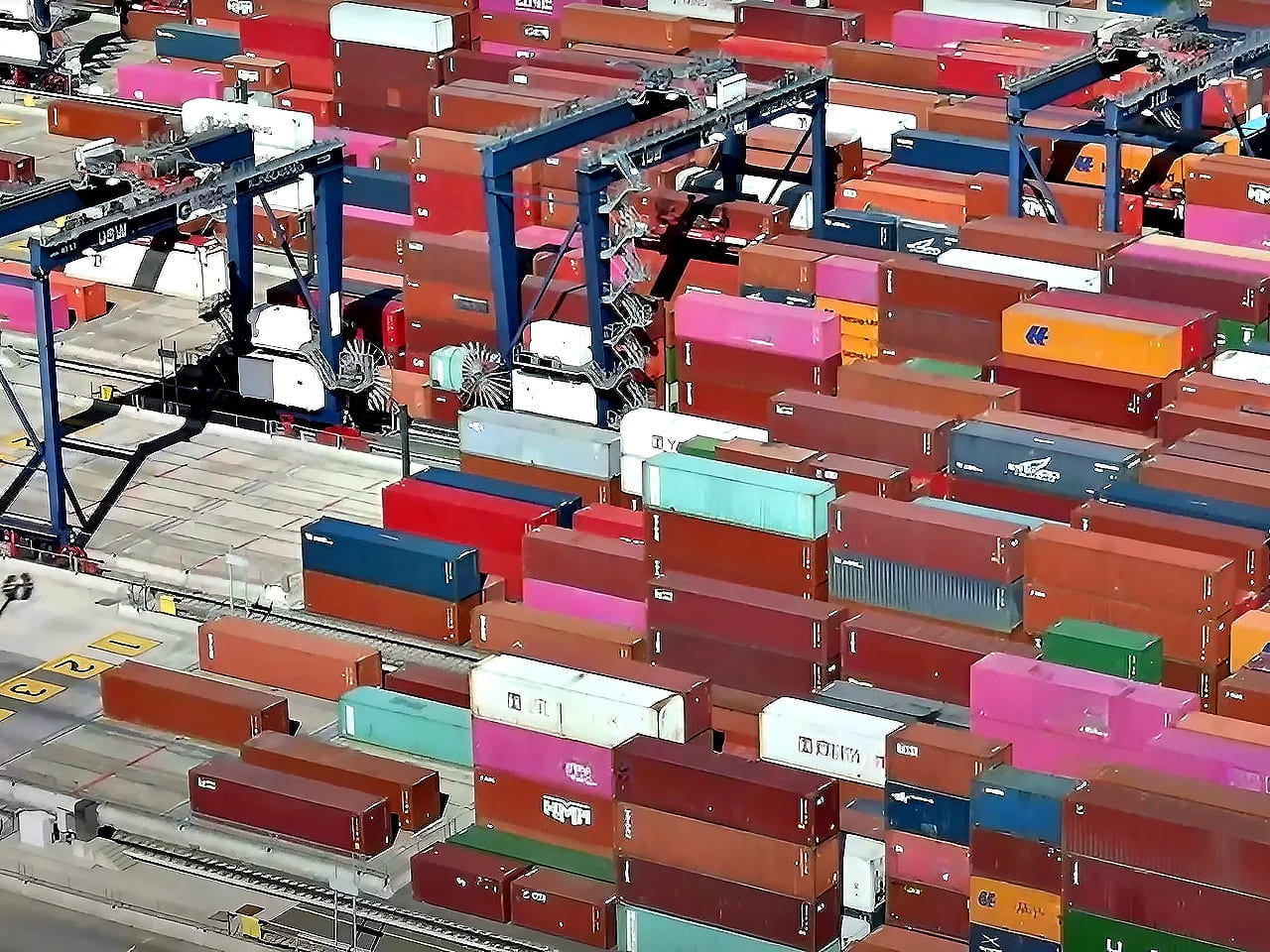
Sea containers are the basis of modern international logistics, providing standardization and security in global transportation. Their use has significantly reduced the time and financial costs of delivery, helping to accelerate world trade and globalization processes.
History and development of shipping containers
The introduction of shipping containers in the mid-20th century radically changed shipping methods. This innovation simplified the process of loading and unloading ships, reduced labor costs and reduced the risk of damage to goods.
The importance of container standardization
Container standardization has had a huge impact on international trade. It made it possible to unify transportation processes, facilitating and speeding up the transportation of goods around the world. Containers have become universal, compatible with various modes of transport, which has led to a reduction in logistics costs and an increase in delivery speed. This contributed to the growth of international trade and the acceleration of globalization of the economy.
Types of shipping containers
In international logistics, many types of sea containers are used, each of which is designed for certain types of cargo and transportation conditions:
Universal containers (Dry Van, DC, DV, GP)
- Sizes: 20-, 40-, 45-foot
- Construction: closed side walls and top, sealed doors
- Application: transportation of a wide range of goods, including industrial goods, food, consumer goods, etc.
Reefer containers (RF)
- Sizes: 20-, 40-, 45-foot
- Construction: closed side walls and top, sealed doors, refrigeration unit
- Application: transportation of perishable goods that require maintaining a certain temperature.
Thermal containers (TC)
Isothermal containers.
- Sizes: 20-, 40-, 45-foot
- Construction: closed side walls and top, sealed doors, thermal insulation
- Application: transportation of goods requiring protection from environmental influences. These include: food, pharmaceuticals, electronics.
Containers for dangerous goods (IBC, IBC, IMO)
- Sizes: 20-, 40-foot
- Design: closed side walls and top, sealed doors, special design ensuring the safety of transportation of dangerous goods
- Application: transportation of dangerous goods in accordance with international regulations
Containers for liquid cargo (ISO Tank Container)
- Sizes: 20-, 40-foot
- Design: sealed containers ensuring the safety of liquid cargo during transportation
- Application: transportation of liquid cargo such as petroleum products, chemicals, etc.
Containers for bulk cargo (ISO Bulk Container)
- Sizes: 20-, 40-, 45-foot
- Design: special hatches and loading devices that provide convenient and quick loading and unloading of bulk cargo
- Application: transportation of bulk goods such as grain, coal, ore, etc.
General cargo containers (Open Top, OT)
- Sizes: 20-, 40-, 45-foot
- Design: open top and side walls, sealed doors
- Application: transportation of goods that cannot be loaded and unloaded through standard container doorways.
Containers with open ends (Flat Rack, FR)
- Sizes: 20-, 40-foot
- Design: open ends, sealed doors
- Application: transportation of large cargo that cannot be loaded and unloaded through standard container doorways.
Containers with a removable roof (Open Top, OT)
- Sizes: 20-, 40-, 45-foot
- Construction: removable roof, sealed doors
- Application: transportation of goods that may be damaged when loading and unloading through standard container doorways.
Each of these container types provides unique capabilities to transport different types of cargo, taking into account their specific requirements such as size, weight, temperature sensitivity and general transport conditions. Choosing the right type of container is a key aspect of efficient and secure international logistics.
Standard dimensions of sea containers
20ft container (20) / Standard / Standart / Dry Cube / Dry Van / General Purpose (ST, DC, DV, GP)
- External dimensions: length: 6058 mm, width: 2438 mm, height: 2591 mm
- Internal dimensions: length: 5898 mm, width: 2352 mm, height: 2393 mm
- Door opening: width 2343 mm, height 2280 mm
- Maximum load capacity, kg: 30480 kg
- Tare weight, kg: 2150 kg
- Payload, kg: up to 28330 kg
- Volume, cubic meters: 33.2 cubic meters
- Number of Euro pallets that can be accommodated, pcs: up to 11
Application: standard 20-foot containers are a universal solution for most types of dry cargo.
These containers are ideal for transporting a variety of goods, including packaged goods, electronics, clothing and other items that require dry storage during transit.
40ft container (40) / Standard / Standart / Dry Cube / Dry Van / General Purpose (ST, DC, DV, GP)
- External dimensions: length: 12192 mm, width: 2438 mm, height: 2591 mm
- Internal dimensions: length: 12032 mm, width: 2352 mm, height: 2393 mm
- Door opening: width 2343 mm, height 2280 mm
- Maximum load capacity, kg: 32500 kg
- Tare weight, kg: 3620 kg
- Payload, kg: up to 28880 kg
- Volume, cubic meters: 67.8 cubic meters
- Number of Euro pallets that can be accommodated, pcs: up to 25
Application: used for transporting a variety of goods in large quantities, including household appliances, furniture, building materials and other large or bulk cargo.
40-foot refrigerated container (40RF) / Standard / Standard 40-foot
- External dimensions: length: 12192 mm, width: 2438 mm, height: 2591 mm
- Internal dimensions: length: 11599 mm, width: 2280 mm, height: 2159 mm
- Door opening: width 2290 mm, height 2264 mm
- Maximum load capacity, kg: 32500 kg
- Tare weight, kg: 4500 kg
- Payload, kg: up to 28000 kg
- Volume, cubic meters: 59.9 cubic meters
- Number of Euro pallets that can be accommodated, pcs: up to 23
- Supported temperature range: from -25ºС to +25ºС
Application: 40ft refrigerated containers are widely used to transport perishable products such as seafood, meat, fruits and vegetables, as well as pharmaceuticals and chemicals that require strict temperature control during transportation.
20-foot container High Cube (20HC) / High / High Cube (HC) 20-foot
- External dimensions: length: 6058 mm, width: 2438 mm, height: 2896 mm
- Internal dimensions: length: 5898 mm, width: 2352 mm, height: 2698 m
- Door opening: width 2343 mm, height 2585 mm
- Maximum load capacity, kg: 30480 kg
- Tare weight, kg: 2320 kg
- Payload, kg: up to 28160 kg
- Volume, cubic meters: 37.4 cubic meters
- Number of Euro pallets that can be accommodated, pcs: up to 11
Application: Containers are often used to transport goods that require additional vertical space, such as light industrial equipment, bulky furniture, and high-stack packaged goods.
45ft container High Cube (45HC) / High
- External dimensions: length: 13716 mm, width: 2438 mm, height: 2896 mm
- Internal dimensions: length: 13556 mm, width: 2352 mm, height: 2698 mm
- Door opening: width 2343 mm, height 2585 mm
- Maximum load capacity, kg: 34000 kg
- Tare weight, kg: 4700 kg
- Payload, kg: up to 29300 kg
- Volume, cubic meters: 86 cubic meters
- Number of Euro pallets that can be accommodated, pcs: up to 33
Application: 45-foot High Cube containers provide large volume and increased loading capacity, making them an ideal choice for transporting large quantities of cargo or large items.
40ft High Cube refrigerated container (40HC RF) / High
- External dimensions: length: 12192 mm, width: 2438 mm, height: 2896 mm
- Internal dimensions: length: 11599 mm, width: 2280 mm, height: 2425 mm
- Door opening: width 2290 mm, height 2557 mm
- Maximum load capacity, kg: 32500 kg
- Tare weight, kg: 4700 kg
- Payload, kg: up to 27800 kg
- Volume, cubic meters: 67.5 cubic meters
- Number of Euro pallets that can be accommodated, pcs: up to 23
- Supported temperature range: from -25ºС to +25ºС
Application: 40ft High Cube refrigerated containers offer increased internal space and high technical capabilities for transporting goods requiring controlled temperatures.
40-foot Open Top container (40OT) / Standard / Standard 40-foot
- External dimensions: length: 12192 mm, width: 2438 mm, height: 2591 mm
- Internal dimensions: length: 12029 mm, width: 2350 mm, height: 2380 mm
- Door opening: width 2238 mm, height 2280 mm
- Roof opening: Length 11552 mm, width 2230 mm
- Maximum load capacity, kg: 32500 kg
- Tare weight, kg: 4050 kg
- Payload, kg: up to 28450 kg
- Volume, cubic meters: 66.8 cubic meters
- Number of Euro pallets that can be accommodated, pcs: up to 25
Application: Standard 40ft Open Top containers are designed for cargo that requires top loading or large vertical space. Ideal for transporting heavy and bulky cargo, such as engineering equipment, construction materials and other cargo that cannot be loaded through conventional container doors.
Selecting a container for different cargo
Selecting the right type of container is a key aspect in international logistics. It depends on a number of factors, including the characteristics of the cargo, its transportation requirements and route specifications.
How to choose the appropriate container type:
- Assess the characteristics of the cargo: size, weight, need for temperature control, resistance to moisture and other factors.
- Consider transportation considerations, such as the need for vertical loading, sensitivity to vibration and shaking.
- Choose according to regulations and standards: make sure the container complies with international safety and transportation regulations.
Examples of using different types of containers:
Universal containers (Dry Van, DC, DV, GP)
Used for transportation of a wide range of goods, including:
- industrial goods, such as machines, equipment, building materials;
- food such as fruits, vegetables, meat, fish;
- consumer goods such as clothing, shoes, household appliances;
- other cargo that does not require special transportation conditions.
Reefer containers (RF)
Used for transportation of perishable goods, such as:
- meat, fish, seafood;
- dairy products;
- vegetables, fruits;
- flowers;
- other cargo that requires maintaining a certain temperature.
Thermal containers (TC)
Used for transportation of goods requiring protection from environmental influences, including:
- food;
- pharmaceuticals;
- electronics;
- other cargo that is sensitive to changes in temperature and humidity.
Containers for dangerous goods (IBC, IBC, IMO)
Used for the transportation of dangerous goods in accordance with international regulations. Dangerous goods include, in particular, explosives, flammable substances, radioactive substances, toxic substances.
Containers for liquid cargo (ISO Tank Container)
Used for transportation of liquid cargo, such as:
- petroleum products;
- chemicals;
- food products;
- other liquid cargo.
Containers for bulk cargo (ISO Bulk Container)
Used for transportation of bulk cargo, such as:
- grain;
- coal;
- ore;
- other bulk cargo.
General cargo containers (Open Top, OT)
Used for transporting goods that cannot be loaded and unloaded through standard container doorways. Such cargo includes, in particular, large cargo, long cargo, cargo with a non-standard shape.
Containers with open ends (Flat Rack, FR)
Used for the transportation of large cargo that cannot be loaded and unloaded through standard container doorways.
Containers with a removable roof (Open Top, OT)
Used for transporting goods that may be damaged during loading and unloading through standard container doorways. Such cargo includes, in particular, fragile cargo and cargo with sharp edges.
Innovations in container transportation
The modern world of international logistics is developing rapidly thanks to new technologies and digitalization. These innovations are aimed at improving the efficiency, transparency and reliability of transportation processes.
New technologies and trends
- Smart containers: equipped with sensors that allow you to monitor conditions inside the container, such as temperature, humidity, and even location in real time.
- Automated cargo handling: Robotic loading and unloading systems speed up cargo handling and reduce the risk of human errors.
- Green technologies: development and use of environmentally friendly materials and technologies to reduce the carbon footprint of the transportation process.
Digitalization in logistics
- Transport management platforms: integration of various stages of the supply chain into a single information system for better planning and management.
- Blockchain: using blockchain technology to increase the transparency and security of logistics operations.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning: using AI to analyze big data, optimize routes and forecast logistics needs.
These innovations not only improve efficiency and safety in international shipping, but also help companies adapt to rapidly changing market demands and increase customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
The efficiency of international logistics largely depends on the competent choice of container. This is a key link that determines not only the safety of the cargo, but also the cost of transportation. Different types of containers offer solutions for a wide range of cargo, providing flexibility and adaptation to a variety of logistics challenges.
Modern technological trends such as smart containers and automated control systems are significantly improving the efficiency of logistics operations. The use of innovations such as IoT, blockchain and artificial intelligence allows companies to increase transparency, control and optimization of their logistics processes.
Ultimately, a competent approach to the selection of containers and the use of advanced technologies in logistics contribute to increasing overall efficiency, reducing costs and strengthening companies' position in the global market. These aspects significantly influence the success of international cargo transportation in the modern economy.

 English
English
 Русский
Русский Español
Español

